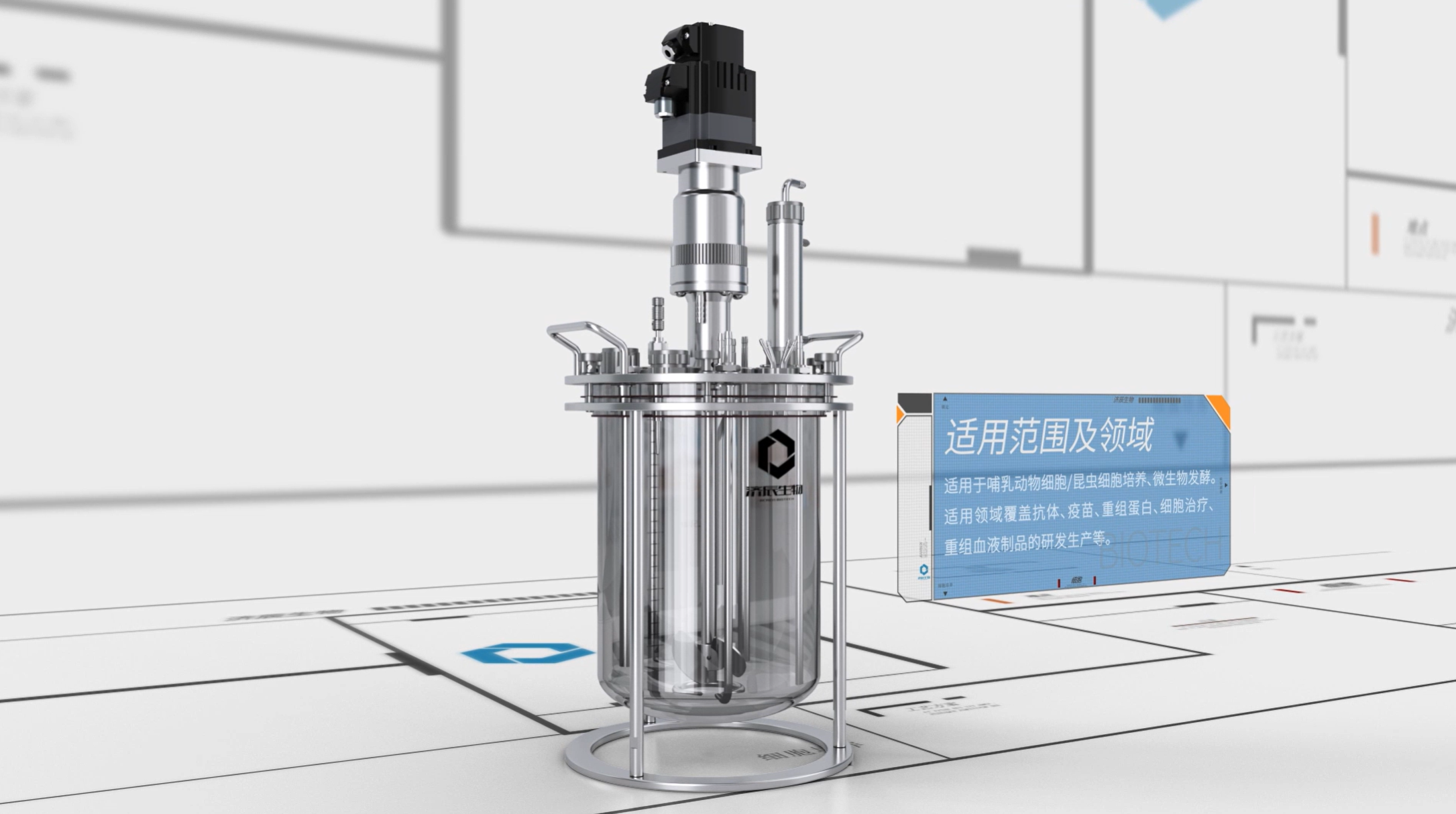
Bioreactor, as an important technology in the field of bioengineering, is changing our life. It can not only produce drugs, food additives and biofuels efficiently, but also play a great role in environmental protection and resource recycling. In this paper, we will provide a comprehensive explanation of bioreactors in terms of their principles, types, operational processes and their applications in various fields.
Basic principles and types of bioreactors
1. Basic principles
The working principle of bioreactors is based on the catalytic action of biocatalysts. These catalysts can be enzymes or microorganisms. Enzymes, as biomolecules, can significantly reduce the activation energy of a chemical reaction and speed up the reaction, while microorganisms, through their metabolic activity, convert raw materials into target products.
2. Types
Based on the biocatalysts, the bioreactors can be classified as follows Types:
(1) Enzyme reactor: using enzymes as catalysts, suitable for fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals and other fields.
(2) Microbial reactor: using microorganisms as catalysts, widely used in food, beverage, environmental protection and other industries.
(3) Animal cell reactor: using animal cells to produce drugs, vaccines and other high value-added products.
(4) Plant cell reactor: production of natural compounds, drugs, etc. through plant cell culture.
Bioreactor operation process
}1. Pre-treatment
Before feeding the feedstock into the bioreactor, pre-treatment such as pulverization, dissolution, sterilization, etc. is required to ensure that the feedstock is suitable for biocatalyst action.
2. Reaction phase
(1) Inoculation: for microbial reactors, it is necessary to inoculate the preferred microbial strain to be inoculated into the reactor.
(2) Cultivation: under suitable conditions of temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, etc., the biocatalyst is allowed to come into full contact with the raw materials to carry out the catalytic reaction.
(3) Control: By monitoring the parameters in the reactor, such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, etc., timely adjustments are made to ensure the smooth progress of the reaction.
3. Post-processing
After the reaction is completed, the products need to be separated and purified. The products need to be post-treated such as separation, purification and drying to obtain the final product.
Applications of bioreactors
1. pharmaceutical field 141}}1. Pharmaceutical field
The applications of bioreactors in the pharmaceutical field mainly include: the production of antibiotics, vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, and genetically engineered drugs.
2. Food field
Using biological reactors to produce fermented foods (e.g. soy sauce, vinegar, yogurt, beer, etc.), food additives (e.g. vitamins, amino acids, etc.).
3. Environmental protection field
Bioreactors are used in the fields of wastewater treatment, exhaust gas treatment, solid waste treatment, etc. have significant advantages and help to realize the recycling of resources.
4. Bioenergy
Bioreactors can be be used to produce renewable energy such as biodiesel, biomass gas, bioethanol, etc. to alleviate the energy crisis.
Bioreactors, as a kind of highly efficient and environmentally friendly technological means, have demonstrated great potential and value for their application in many fields. With the continuous progress of biotechnology, the research and development and application of bioreactors will be more in-depth, making greater contributions to the development of human society. Understanding the working principle and application of bioreactors will help us to better grasp this technology and promote its wide application in our country and the world.