Bioreactors, as a device that utilizes biocatalysts (enzymes or microorganisms) to convert biomass into useful products, have come to play an important role in the fields of medicine, food, and environmental protection. So, how exactly does a bioreactor work? This article will answer this question for you in detail.
Basic Principles of Bioreactors
1. The Role of Biocatalysts
The core of bioreactors lies in the biocatalysts, which mainly include enzymes and microorganisms. Enzymes are highly specialized biomolecules that accelerate the rate of chemical reactions, while microorganisms have a powerful metabolic ability to convert biomass into target products.
2. The basic structure of a bioreactor
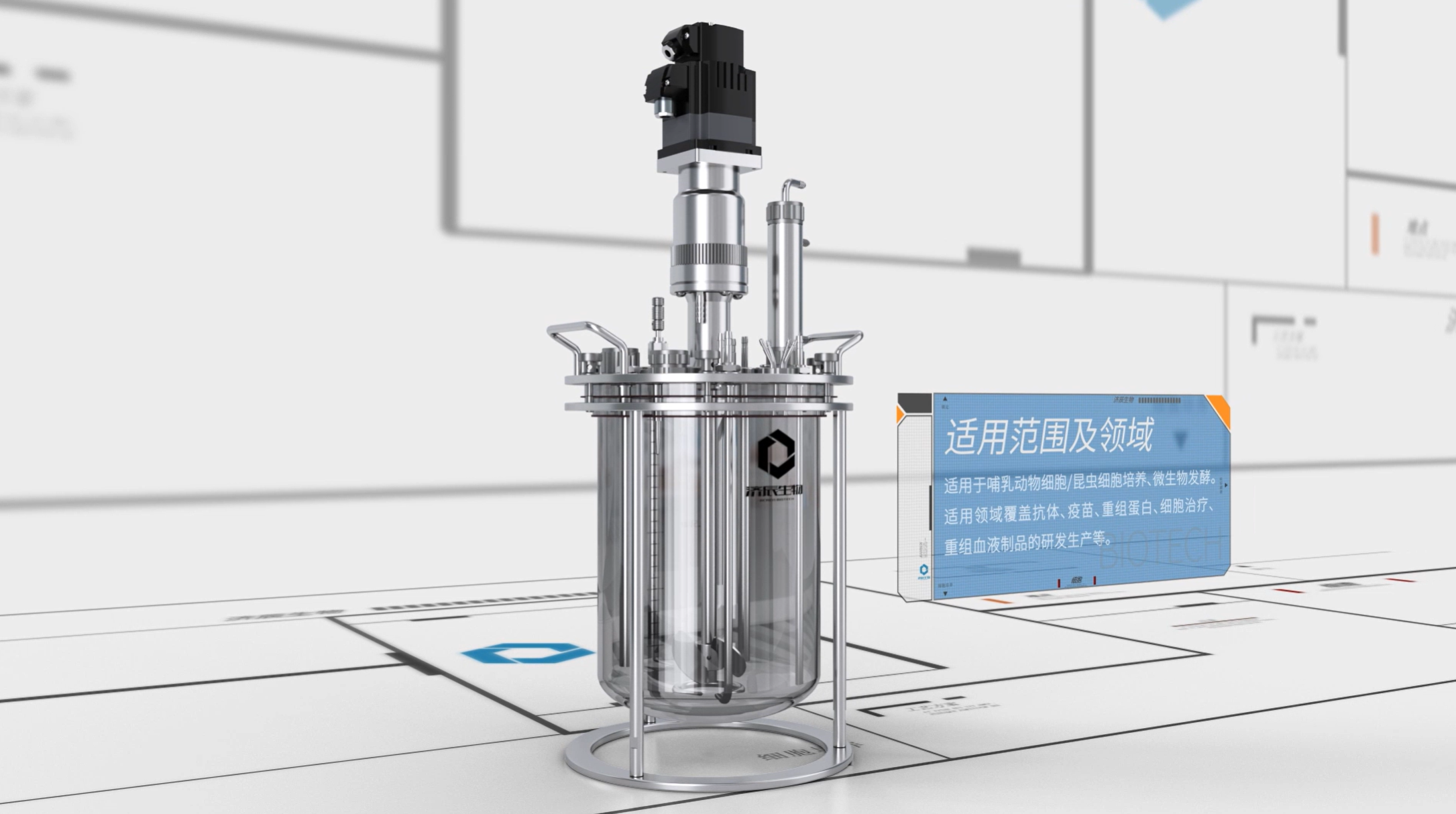
A bioreactor usually consists of the following parts : reactor body, feeding system, discharging system, control system, temperature regulation system, and so on. The reactor body is the place where the biocatalyst reacts with the biomass, and its design directly affects the reaction effect.
Working flow of the bioreactor
}1. Feeding
First, raw materials containing biomass are fed into the bioreactor through a feeding system. The biomass may be a solid, a liquid or a gas, such as crop residue, wastewater, carbon dioxide, and the like.
2. Reaction
Inside the bioreactor, the biomass is in full contact with the biocatalyst and a chemical reaction occurs. The specific processes are as follows:
(1) Enzyme-catalyzed reaction: enzymes accelerate the rate of chemical reaction by reducing the activation energy of the reaction. For example, in winemaking, enzymes convert starch into sugar.
(2) Microbial metabolism: microorganisms grow, reproduce, and metabolize under suitable environmental conditions by ingesting organic matter from biomass to produce target products. For example, in wastewater treatment, microorganisms decompose organic pollutants into inorganic substances.
3. Discharge
After the reaction is completed, the target products generated are discharged from the bioreactor through a discharge system. Depending on the nature of the products, different discharge methods can be used, such as solid-liquid separation and gas collection.
4. Control and regulation
In order to ensure the efficient operation of the bioreactor, it is necessary to control the bioreactor. reactor operates efficiently, the following parameters need to be monitored and adjusted in real time:
(1) Temperature: the activity of the biocatalyst is greatly affected by the temperature, and the appropriate temperature is conducive to the improvement of the reaction rate. The temperature adjustment system can adjust the temperature in the reactor according to the actual demand.
(2) pH: The growth of microorganisms and enzyme activity have certain requirements on pH. The pH value in the reactor is maintained within a suitable range by adjusting the feed composition or adding acid and alkaline substances.
(3) Oxygen supply: for aerobic microorganisms, it is necessary to ensure sufficient oxygen supply. By controlling the air intake and stirring speed, the uniform distribution of oxygen in the reactor is realized.
1. Pharmaceutical field: Production of antibiotics, vaccines, biopharmaceuticals and so on.
2. Foodstuffs field: Fermentation to produce soy sauce, vinegar, yogurt, beer, etc.
3. Environmental protection field: Treatment of wastewater and waste gas, and realization of resource recycling.
4. Bio-energy: Producing renewable energy sources such as biodiesel and biomass gas.
Bioreactor as a kind of high-efficiency, environmentally friendly technical means, has a wide range of application prospects in the economic and social development of China. Through a deep understanding of the working principle of bioreactor, it helps us to better play its role and create more value for human beings. With the continuous development of biotechnology, bioreactors will play a more important role in the future.