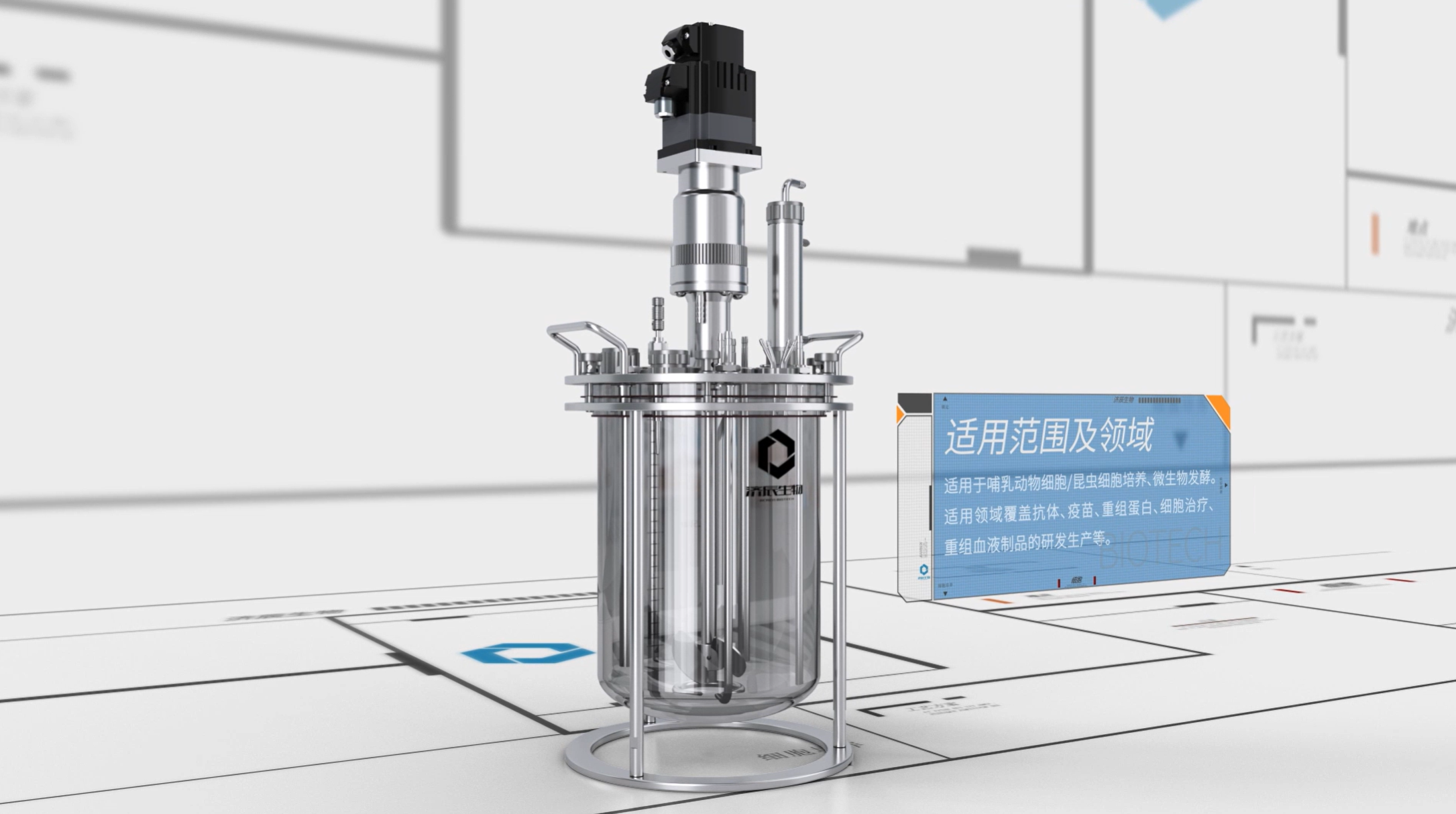
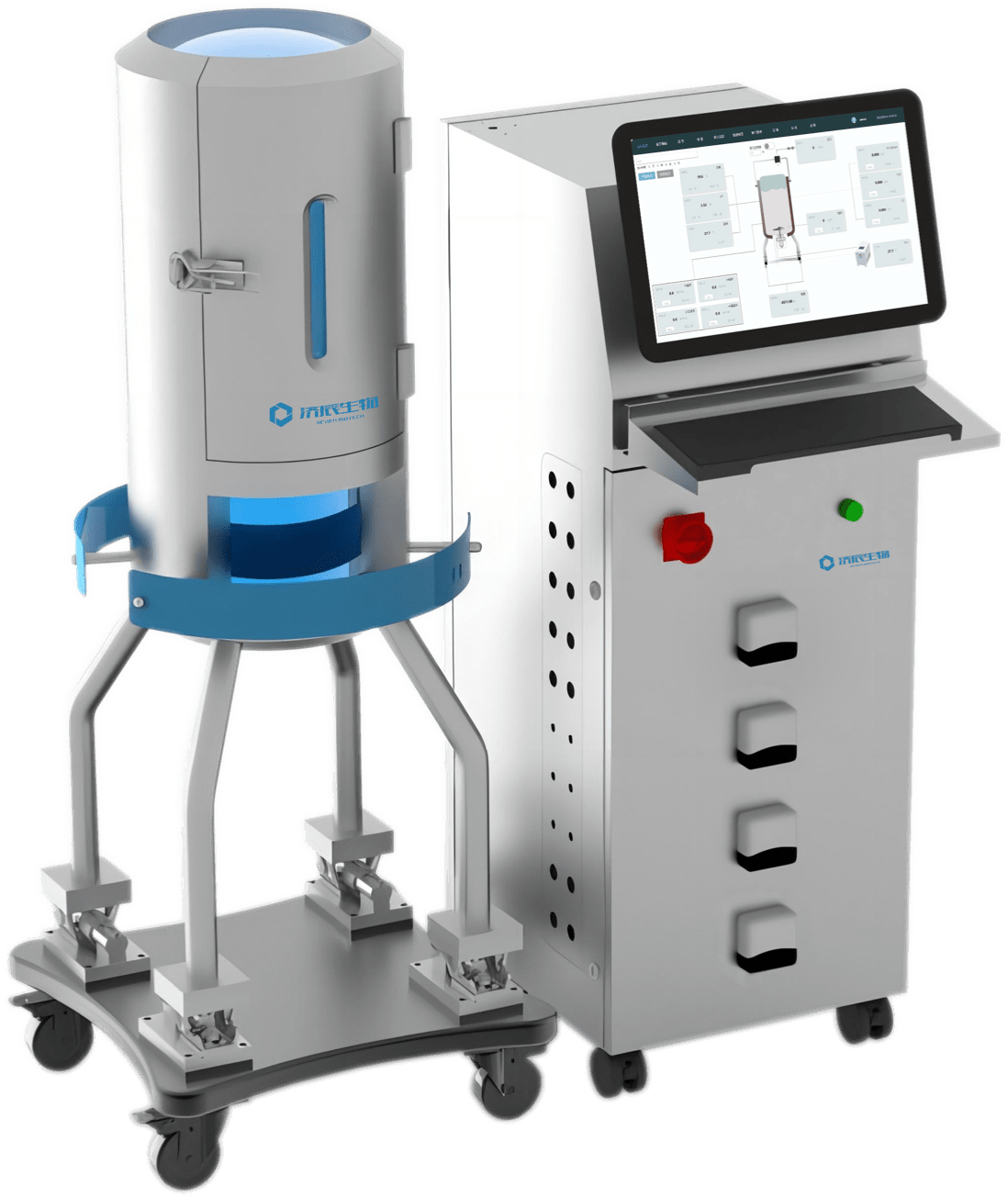
Bioreactor structure
Generally common mechanical stirring reactor structure for the vessel, baffle, agitator, air distribution device, shaft seal, transmission, heat exchange device, defoamer, and so on. .
where the vessel is the main body of the bioreactor and is used to hold the organisms, the medium, and the conditions required for the reaction. The agitator, in turn, is used to maintain the culture medium in a homogeneous state of suspension and to promote adequate contact between the organisms and the culture medium. The
temperature control device ensures that the temperature inside the reactor is always maintained within a suitable range to meet the needs of the growth and reaction of the organism. The inlet and outlet ports are used to add media and collect reaction products, while the gas inlet and outlet ports are used to control the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide inside the reactor. The sensors and control system are then able to monitor and regulate the parameters inside the reactor in real time to ensure the stability of the reaction.
Principles of a bioreactor
And the next thing to talk about is the principles of a bioreactor, which involves a number of aspects such as reaction, mass transfer and energy conversion.
The reactions of a bioreactor are mainly based on the provision of a suitable extracorporeal environment for the growth, metabolism, and product generation of the biological system. In the reactor, the biological system usually includes microorganisms, cell cultures or enzymes, etc., which carry out metabolic activities in a suitable medium, and adequate oxygen delivery and uniform distribution of nutrients are maintained by an agitation device. Meanwhile, the constant temperature and pH inside the reactor are maintained by a temperature control device and a pH adjustment system to provide a stable growth environment for the biological system.
Mass transfer refers to the process of substrate and product transfer inside the reactor, including mass transfer resistance and rate. Mass transfer resistance affects the reaction rate, substrate utilization, and product concentration, and this resistance generally arises from the diffusion resistance, solubility, and mass transfer resistance of the substrate and products in the reaction. The rate of mass transfer, on the other hand, can be affected by various factors such as stirring speed, temperature, and substrate concentration.
Energy conversion involves heat-absorbing and heat-exchanging reactions during a reaction. An absorptive reaction causes an organism to provide the energy needed for metabolism by absorbing external heat, promoting growth and metabolism. An exothermic reaction occurs when the reactants release heat energy during metabolism, and this heat energy serves as the thermal energy requirement for the reaction.
So what should be done to control the normal reaction of the reactor?
Provision of appropriate substrates:Bioreactors safeguard the growth and metabolism of organisms by providing them with appropriate substrates. These substrates can be organic matter, inorganic salts, etc., depending on the needs of the organism.
Control of environmental conditions: The bioreactor creates an environment suitable for the growth and metabolism of the organisms by controlling the environmental conditions. The needs of the organisms are met by means of regulating temperature, pH, oxygen concentration, and nutrient concentration.
Maintaining Mixing and Oxygen Transfer: Bioreactors use stirring and aeration and other methods to allow the reactants and organisms to be mixed uniformly, thus enhancing the mass transfer efficiency. For aerobic organisms, sufficient oxygen is also provided to meet the needs of biological respiration.
Control of outputs and by-products: The bioreactor controls the generation of outputs and by-products by controlling the parameters (e.g., temperature, pH, nutrient concentration, etc.) during the reaction. Optimization of these parameters can effectively improve product yield and selectivity.
Monitoring and regulation: Bioreactors are generally equipped with sensor devices to monitor important parameters such as temperature, pH, oxygen concentration, and density of organisms in the reaction. Based on the feedback signals from the sensors, regulation is carried out to keep it in the optimal working condition.
In short, bioreactors can realize the efficient growth of biological systems and mass production of products through the precise control of the culture medium, experimental environmental conditions, etc., which provides an important support for the development of bioengineering and biopharmaceutical fields.