With the rapid development of biotechnology, fermentation technology has been increasingly widely used in the pharmaceutical industry. This paper mainly discusses the new applications, development trends, challenges and innovation strategies of fermentation technology in the pharmaceutical industry, aiming to provide reference for China's fermentation pharmaceutical industry.
Fermentation technology is a method of utilizing microorganisms' metabolism for the production of useful substances, which has the advantages of easy operation, low production cost, and rich variety of products. In the pharmaceutical industry, fermentation technology has become a key link in the production of antibiotics, vaccines, bioactive substances and so on. With the continuous progress of science and technology, the application of fermentation technology in the pharmaceutical industry continues to innovate, injecting new vitality into the development of China's pharmaceutical industry.
New applications of fermentation technology in the pharmaceutical industry
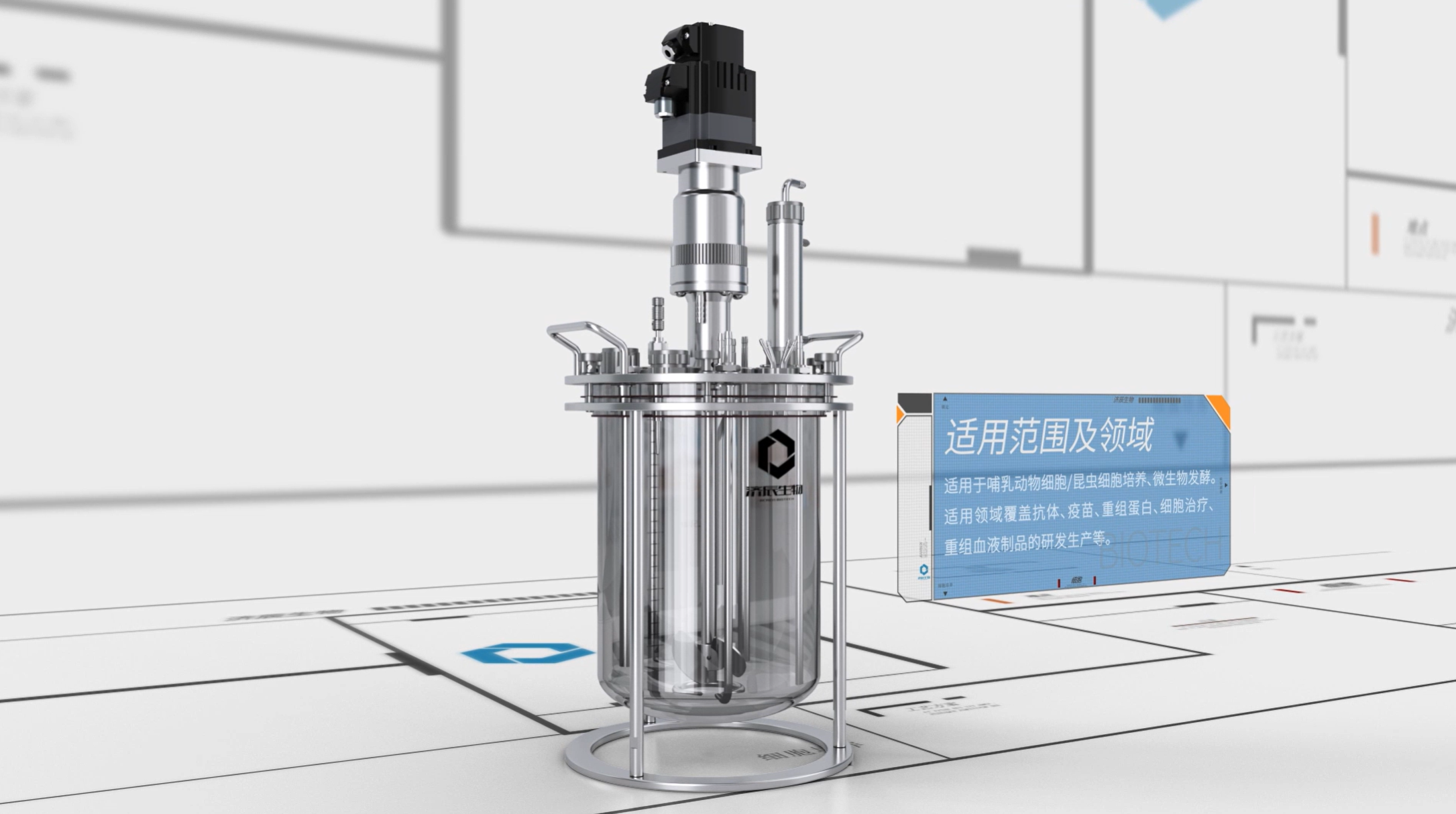
1. Microbial Pharmaceuticals: the production of antibiotics, vaccines, hormones, and other drugs through the fermentation technology has become the core technology in the field of microbial pharmaceuticals.
2. Cell culture: large-scale cultivation of animal cells and plant cells using fermentation technology for the production of vaccines, antibodies, biologically active substances and so on.
3. Enzyme engineering: production of enzyme preparations by fermentation technology, widely used in pharmaceutical, food, environmental protection and other fields.
4. Genetic engineering: Fermentation technology provides an important means for the production of genetically engineered drugs, such as recombinant proteins and antibodies.
The development trend of fermentation technology in the pharmaceutical industry
1. Green fermentation: the use of environmentally friendly fermentation processes to reduce energy consumption, reduce waste emissions, and achieve sustainable development.
2. Intelligent fermentation: use modern information technology to realize real-time monitoring and automatic control of the fermentation process and improve production efficiency.
3. Integrated fermentation: combining fermentation technology with other bioengineering technologies to form an efficient and low-cost biomanufacturing system.
4. Microbial Diversity Exploitation: Mining microbial resources and screening strains with specific functions to provide more possibilities for the pharmaceutical industry.
Challenges of fermentation technology in the pharmaceutical industry
1. Limited strain resources: scarcity of high-yield, high-quality, and contamination-resistant strains restricts the development of fermentation technology.
2. Difficulty in controlling the fermentation process: During the fermentation process, the growth of strains and the synthesis of products are affected by many factors, and it is difficult to realize precise control.
3. Unstable product quality: the quality of fermentation products is affected by factors such as strains and fermentation conditions, and the product quality fluctuates greatly.
4. Higher production cost: large investment in fermentation equipment, high cost of energy consumption and raw materials in the production process.
Innovation strategy of fermentation technology
1. Strain innovation: adopt genetic engineering technology to construct high-yield, high-quality and anti-pollution engineering strains.
2. Technological innovation: optimize the fermentation conditions, improve the control level of fermentation process, and realize green and intelligent fermentation.
3. Equipment innovation: research and development of high-efficiency, low-cost fermentation equipment to reduce production costs.
4. Product innovation: Expand the application fields of fermentation products and improve the added value of products.
5. Management innovation: establish a sound fermentation technology management system to improve the overall competitiveness of the industry.
The application and innovation of fermentation technology in the pharmaceutical industry are of great significance. In the face of challenges, China should increase research and development efforts to promote fermentation technology innovation and provide strong support for the pharmaceutical industry. At the same time, strengthen the cooperation between industry, academia and research, cultivate high-quality talents, and help China's fermentation and pharmaceutical industry to realize high-quality development.