What is the definition of bioprocessing and what is the process?
Bioprocessing is a technological activity in which bioengineers manipulate living organisms and systems found in nature to achieve research and industrial purposes. The process involves the use of microbial, animal, plant and fungal cells, as well as biological components such as enzymes, as catalysts or raw materials for chemical production.
The basic process of bioprocessing can be summarized in the following steps:
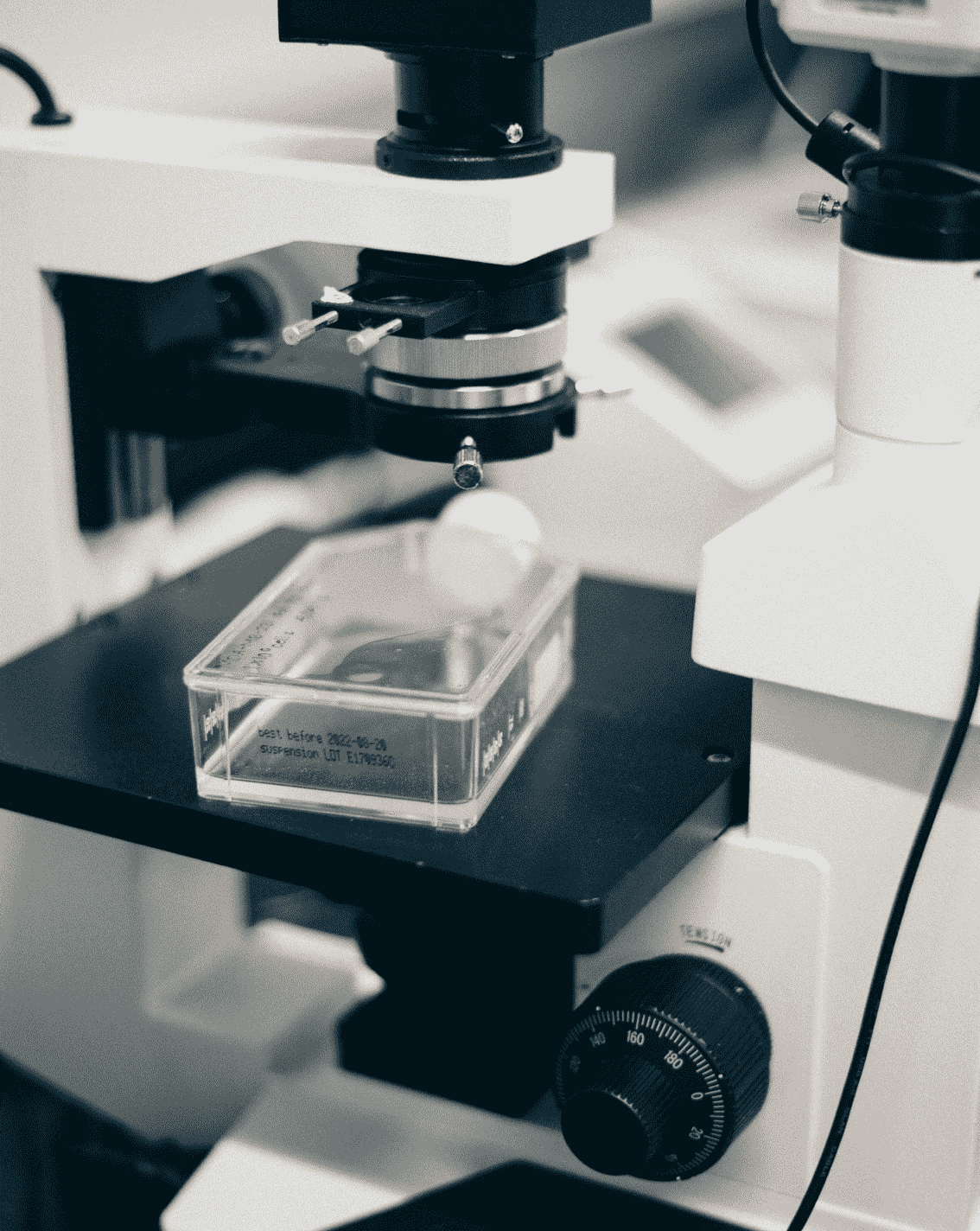
Scientists select suitable biological systems, substrates, and target products; genetic modification, kinetic simulations, and small-scale experiments; scaling up of operating units and catalytic processes in bioreactors; extraction of samples by filtration and purification; and final recovery of products and disposal of wastes. This process follows the basic principles of planning and implementation, and continuous monitoring is implemented throughout the process.
What are the upstream and downstream operations of bioprocessing?
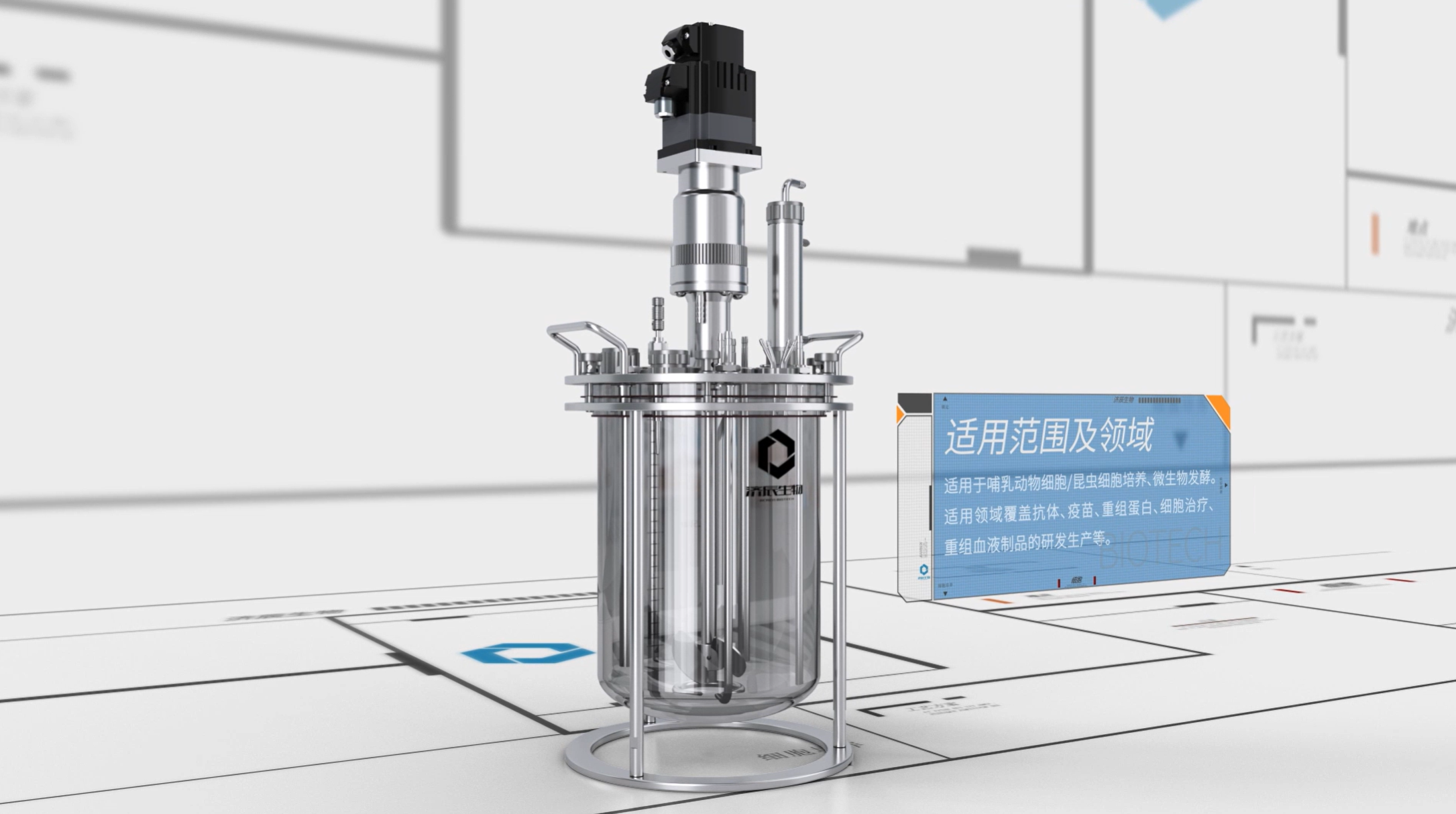
Upstream processing is the first stage of bioprocessing, where bioengineers identify biocatalysts or systems that can be used for industrial purposes and design industrial environments to support the desired metabolic activities. This includes genetic engineering modifications to give host organisms the properties required for industrial production, and kinetic analysis through mathematical modeling to characterize the various properties of biological systems.
Downstream processing occurs after the catalytic process and is aimed at recovering the final product.
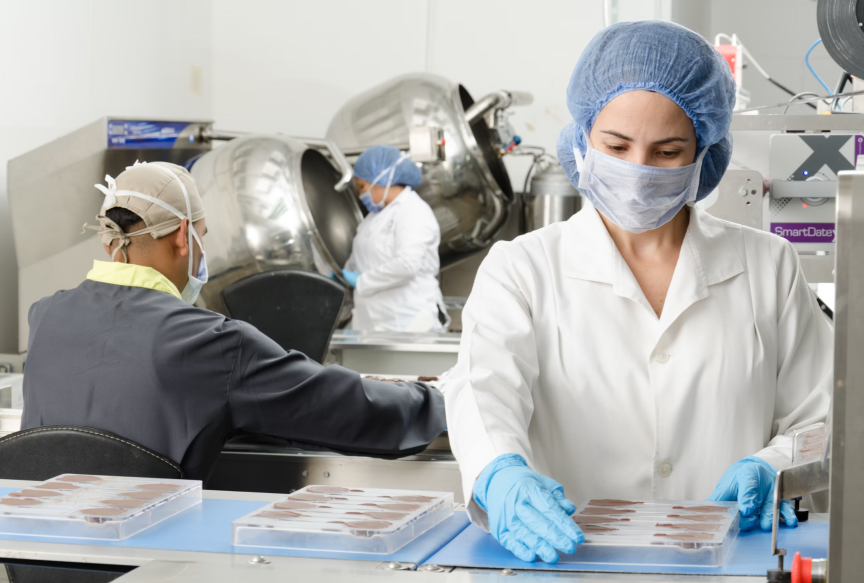
The unit operations used in this stage depend on the location and form of the product in the feedstock. The challenge with downstream processing is that techniques such as filtration and purification that have been successful at the laboratory scale can be difficult and costly to apply on a large scale.
What are the areas where bioprocessing has applications?
Bioprocessing technology has a wide range of applications in a number of fields, including food science, the pharmaceutical industry, and the production of biofuels. For example, in the food industry, bioprocessing is used for the production of fermented foods and enzymes; in the pharmaceutical field, bioprocessing is an important tool for the production of drugs and biologics; and in the energy field, bioprocessing helps to convert organic materials into biofuels and reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
What is the definition and process of bioprocessing?
Bioprocessing is a technological activity in which bioengineers manipulate living organisms and systems found in nature for research and industrial purposes. The process involves the use of microbial, animal, plant, and fungal cells, as well as biological components such as enzymes, as catalysts or raw materials for chemical production.
The basic process of bioprocessing can be summarized in the following steps:
{{{ This process follows the basic principles of planning and implementation, and continuous monitoring is implemented throughout the process.
What are the upstream and downstream operations of bioprocessing?
Upstream processing is the first stage of bioprocessing, where bioengineers identify biocatalysts or systems that can be used for industrial purposes and design industrial environments to support the desired metabolic activities. This includes genetic engineering modifications to give host organisms the properties required for industrial production, and kinetic analysis through mathematical modeling to characterize the various properties of biological systems.
Downstream processing occurs after the catalytic process and is aimed at the recovery of the final product.
The unit operations used in this stage depend on the location and form of the product in the feedstock. The challenge with downstream processing is that techniques such as filtration and purification that have been successful at the laboratory scale can be difficult and costly to apply on a large scale.
What are the areas where bioprocessing has applications?
Bioprocessing technology has a wide range of applications in a number of fields, including food science, the pharmaceutical industry, and the production of biofuels. For example, in the food industry, bioprocessing is used for the production of fermented foods and enzymes; in the pharmaceutical field, bioprocessing is an important tool for the production of drugs and biologics; and in the energy field, bioprocessing helps to convert organic materials into biofuels and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
What are the definitions and processes of bioprocessing?
Bioprocessing is a technological activity in which bioengineers manipulate living organisms and systems found in nature for research and industrial purposes. The process involves the use of microbial, animal, plant, and fungal cells, as well as biological components such as enzymes, as catalysts or raw materials for chemical production.
{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{{ }Scientists select suitable biological systems, substrates, and target products; perform genetic modifications, kinetic simulations, and small-scale experiments; scale up operating units and catalytic processes in bioreactors; extract samples through filtration and purification; and ultimately recycle the products and dispose of the waste. This process follows the basic principles of planning and implementation, and continuous monitoring is implemented throughout the process.
What are the upstream and downstream operations of bioprocessing?
Upstream processing is the first stage of bioprocessing, where bioengineers identify biocatalysts or systems that can be used for industrial purposes and design industrial environments to support the desired metabolic activities. This includes genetic engineering modifications to give host organisms the properties required for industrial production, and kinetic analysis through mathematical modeling to characterize the various properties of biological systems.
Downstream processing occurs after the catalytic process and is aimed at the recovery of the final product.
The unit operations used in this stage depend on the location and form of the product in the feedstock. The challenge with downstream processing is that techniques such as filtration and purification that have been successful on a laboratory scale can be difficult and costly to apply on a large scale.
What are the areas where bioprocessing has applications?
Bioprocessing technology has a wide range of applications in a number of fields, including food science, the pharmaceutical industry, and the production of biofuels. For example, in the food industry, bioprocessing is used for the production of fermented foods and enzymes; in the pharmaceutical field, bioprocessing is an important tool for the production of drugs and biologics; and in the energy field, bioprocessing helps to convert organic materials into biofuels and reduce the dependence on fossil fuels.
}What is the definition and process of biological processing?
Bioprocessing is a technological activity in which bioengineers manipulate living organisms and systems found in nature to achieve research and industrial purposes. The process involves the use of microbial, animal, plant, and fungal cells, as well as biological components such as enzymes, as catalysts or raw materials for chemical production.
The basic process of bioprocessing can be summarized in the following steps:
}Scientists select suitable biological systems, substrates, and target products; perform genetic modifications, kinetic simulations, and small-scale experiments; scale up operating units and catalytic processes in bioreactors; extract samples through filtration and purification; and ultimately recycle the products and dispose of the waste. This process follows the basic principles of planning and implementation, and continuous monitoring is implemented throughout the process.
What are the upstream and downstream operations of bioprocessing?
Upstream processing is the first stage of bioprocessing, where bioengineers identify biocatalysts or systems that can be used for industrial purposes and design industrial environments to support the desired metabolic activities. This includes genetic engineering modifications to give the host organism the properties required for industrial production, and kinetic analysis through mathematical modeling to characterize the various properties of the biological system.
Downstream processing occurs after the catalytic process and is aimed at the recovery of the final product.
The unit operations used in this stage depend on the location and form of the product in the feedstock. The challenge with downstream processing is that techniques such as filtration and purification that have been successful at the laboratory scale can be difficult and costly to apply on a large scale.
What are the areas where bioprocessing has applications?
Bioprocessing technology has a wide range of applications in a number of fields, including food science, the pharmaceutical industry, and the production of biofuels. For example, in the food industry, bioprocessing is used for the production of fermented foods and enzymes; in the pharmaceutical field, bioprocessing is an important tool for the production of drugs and biologics; and in the energy field, bioprocessing helps to convert organic materials into biofuels and reduce the dependence on fossil fuels.