The biopharmaceutical industry, as a strategic emerging industry in China, has achieved world-renowned results in recent years. As a key equipment in the biopharmaceutical process, bioreactor is of great significance for improving production efficiency, reducing cost and ensuring product quality. This paper will introduce the working principle of bioreactor and its application in biopharmaceutical industry in detail.
Bioreactor Overview
Bioreactor is a vessel equipment used for biochemical reactions, which provides a suitable place for microorganisms, cells, and other organisms to grow, reproduce, and metabolize by simulating the environment inside the organism. According to the different organisms, bioreactors can be divided into microbial reactors, cellular reactors, tissue reactors and so on. According to the different structure and working principle of the reactor, it can be divided into stirred bioreactors, air-lift bioreactors, immobilized cell reactors and so on.
Working Principle of Bioreactors
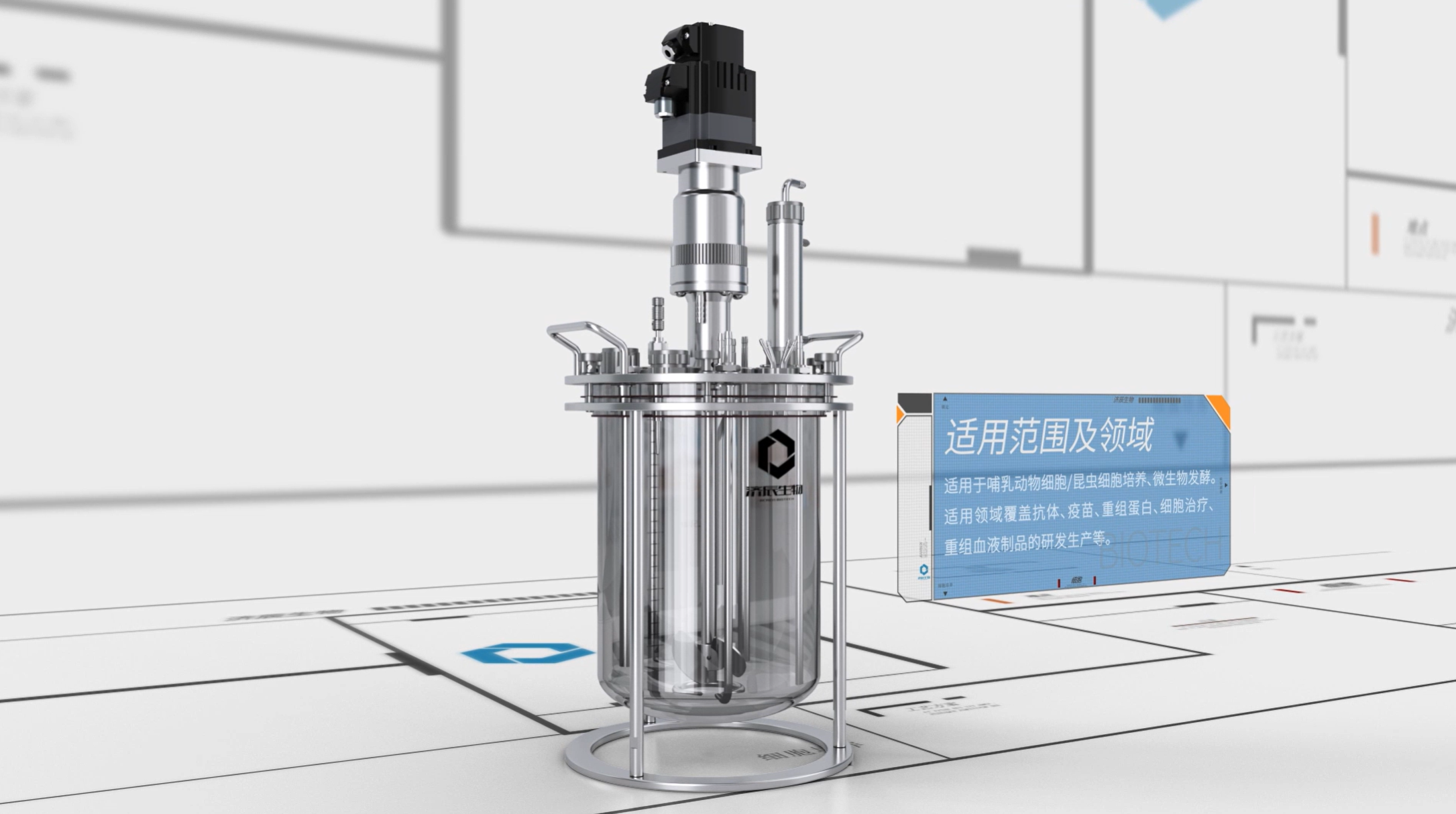
1. Agitated Bioreactor
Stirred bioreactor (STR) is the most widely used type of bioreactor. Its working principle is as follows:
(1) Mixing: Through the rotation of the stirring paddle, the liquid in the reactor generates a vortex, which realizes the full mixing of oxygen, nutrients and organisms.
(2) Mass transfer: the shear force generated by the rotation of the stirring paddle helps the transfer of oxygen and nutrients to the surface of the organisms, and improves the metabolic rate of the organisms.
(3) Heat transfer: through the jacket or built-in coil, etc., to realize the regulation of temperature in the reactor, to ensure the stability of the growth environment of the organism.
2. Gas-ascending bioreactor
A gas-ascending bioreactor (ALR) utilizes kinetic energy generated by the rising gas to realize the circulation of liquid. The working principle is as follows:
(1) Gas injection: gas is injected into the bottom of the reactor through a gas distributor to form bubbles.
(2) Liquid circulation: during the rise of the bubbles, the surrounding liquid is driven upward, forming a circulation.
(3) Mass and heat transfer: during the rising process of the bubbles, the mixing of oxygen, nutrients and organisms is realized, while heat exchange is realized through the friction of the bubbles.
3. Immobilized cell reactor
The immobilized cell reactor is to immobilize the cells on the carrier to realize the immobilized growth of the organism. The working principles are as follows:
(1) Cell fixation: cells are adsorbed or embedded in a carrier to achieve immobilization.
(2) Biological reaction: immobilized cells grow, multiply and metabolize on the surface of the carrier.
(3) Product separation: the product is separated from the cells by filtration and centrifugation.
Bioreactors in the biopharmaceutical industry
1. Microbial fermentation for antibiotic production
Bioreactors are of great importance in antibiotic production. The antibiotic yield can be improved by regulating the temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen and other conditions in the reactor.
2. Plant and animal cell culture for the production of bioproducts
Bioreactors can be used for plant and animal cell culture for the production of bioproducts, such as vaccines, antibodies, hormones and so on. By optimizing the reactor structure and operating parameters, the cell growth rate and product concentration can be increased.
3. Enzyme-catalyzed reactions for the production of drug intermediates
Bioreactors can be used for enzyme-catalyzed reactions to produce drug intermediates. Enzyme stability and catalytic efficiency are improved by immobilized enzyme technology.
4. Biomass conversion for the production of biofuels
Bioreactors play a key role in biomass conversion processes, such as biomass hydrolysis and fermentation. The biofuel yield is increased by optimizing the reactor design.
Bioreactors have been increasingly used in the biopharmaceutical industry, and their working principle and performance have an important impact on the production process. With the continuous development of biotechnology, bioreactors will continue to improve and provide stronger support for the biopharmaceutical industry.