Overview of cell culture techniques
1.1 Definition and history
Cell culture is a technique that mimics the environment of an organism in vitro to allow cells to survive, grow and multiply. The technique originated in the late 19th century and has become an integral part of the biomedical field after more than a hundred years of development.
1.2 Importance and Applications
Cell culture has a wide range of applications in the fields of drug discovery and development, disease modeling, genetic engineering, and tissue engineering. It provides a platform for scientists to study cell behavior and biological processes under controlled conditions.
1.3 Cell Culture Methods
- Primary Culture : Cells are directly isolated from tissues for cultivation and the biological properties of the original tissues are maintained.
- Passage culture: the primary cells are passaged several times to obtain a sufficient number of cells for experiments.
- Stem cell culture: targeting stem cells with self-renewal and differentiation potential for regenerative medicine and disease treatment research.
Concept of one-stop bioprocess technology solutions
2.1 Conceptual connotation
One-stop bioprocess technology Solution refers to a service system that provides all-round support for cell culture from equipment, reagents, culture media to process optimization.
2.2 Advantage Analysis
- Improvement of Efficiency : Integrated equipment and process design, simplify operation steps and shorten experiment cycle.
- Reducing costs: Reducing unnecessary waste by optimizing resource allocation and use.
- Ensure accuracy and reproducibility: Standardized operating procedures and high-quality reagents ensure the reliability of experimental results.
Key technologies and equipments in cell culture
3.1 Key equipments
- CO2 incubator : provides constant temperature, humidity, and CO2 concentration to simulate the in vivo environment for cell growth.
- Centrifuge: used for cell isolation and purification.
- Biological Safety Cabinets: for cell manipulation under aseptic conditions to prevent contamination.
- Shaker: Provides a constant rate of oscillation and promotes adequate contact between cells and culture medium.
3.2 Role of equipment in various stages of cell culture
- Cell separation : utilizes centrifuges, filters, and other equipment to separate specific types of cells.
- Cell modification: gene transfectors, electroporators, etc. are used for gene editing of cells.
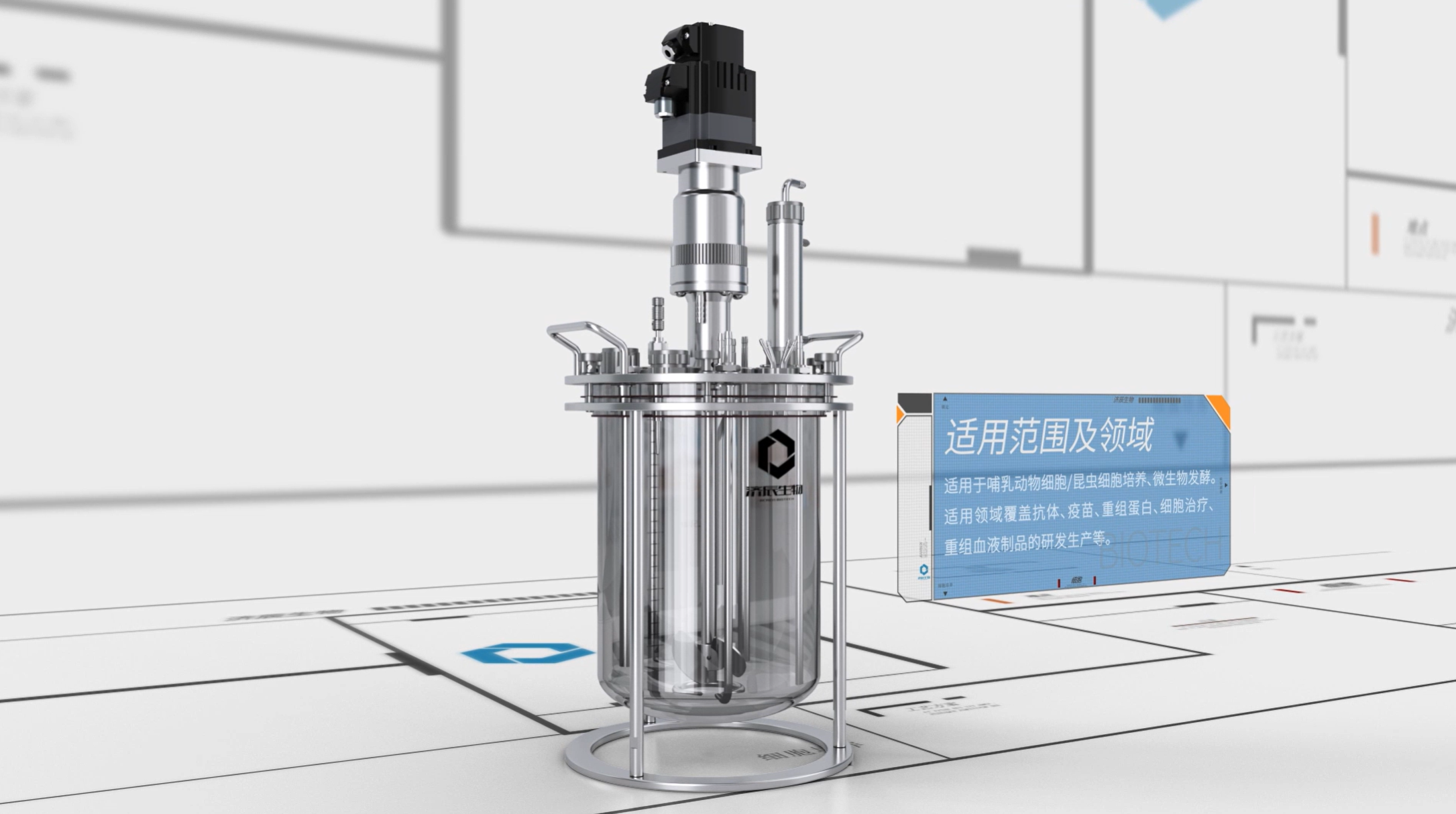
- Cell expansion: scale-up of cell culture by bioreactors and other equipment.
- Cell cryopreservation: long-term preservation of cells using equipment such as liquid nitrogen tanks.
Optimization and innovation of cell culture processes
4.1 Technological innovation
- }improvements in culture media: development of serum-free, animal-derived component-free media to reduce variability and risk of potential pathogens.
- Cell culture environment control: real-time monitoring and regulation of culture conditions using sensors and control systems.
4.2 Scientific research achievements and technological advances
- Automation and digitization : automated cell culture system, digital monitoring platform are applied to improve the accuracy and efficiency of experiments.
Case Studies and Practical Applications
5.1 Specific Cases
- Biopharmaceuticals: production of biopharmaceuticals such as vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and other biopharmaceuticals using cell culture technology.
- Research: researching biological problems such as cell signaling and cell cycle regulation through cell culture.
- clinical treatment: stem cell transplantation to treat hematological disorders, burns and other diseases.
Future Trends and Challenges
6.1 Challenges Ahead
- Cost control: reducing the cost of equipment and reagents to make cell culture technology more widely available.
- Process standardization: establish unified operation procedures and quality standards, and improve the comparability of experimental results.
6.2 Development trend
- Technological innovation: develop new cell culture technologies, such as 3D cell culture, micro fluid cell culture, etc.
- Market Opportunities: With the rapid development of the biopharmaceutical industry, the market demand for cell culture technology will continue to grow.
Through the detailed elaboration of the above six aspects, this article provides a comprehensive analysis of the application of one-stop bioprocess technology solutions in cell culture. We hope these contents can satisfy your need for a long article.