Adherent wall cell culturators are indispensable tools in the biomedical field, which provide powerful support for cell biology, drug discovery, tissue engineering and other fields. In this paper, we will discuss in detail the principles, types, challenges in biomedical applications, and development prospects of adherent wall cell culturators.
Basic Principles and Types of Adherent Cell Culturators
- Basic Principles
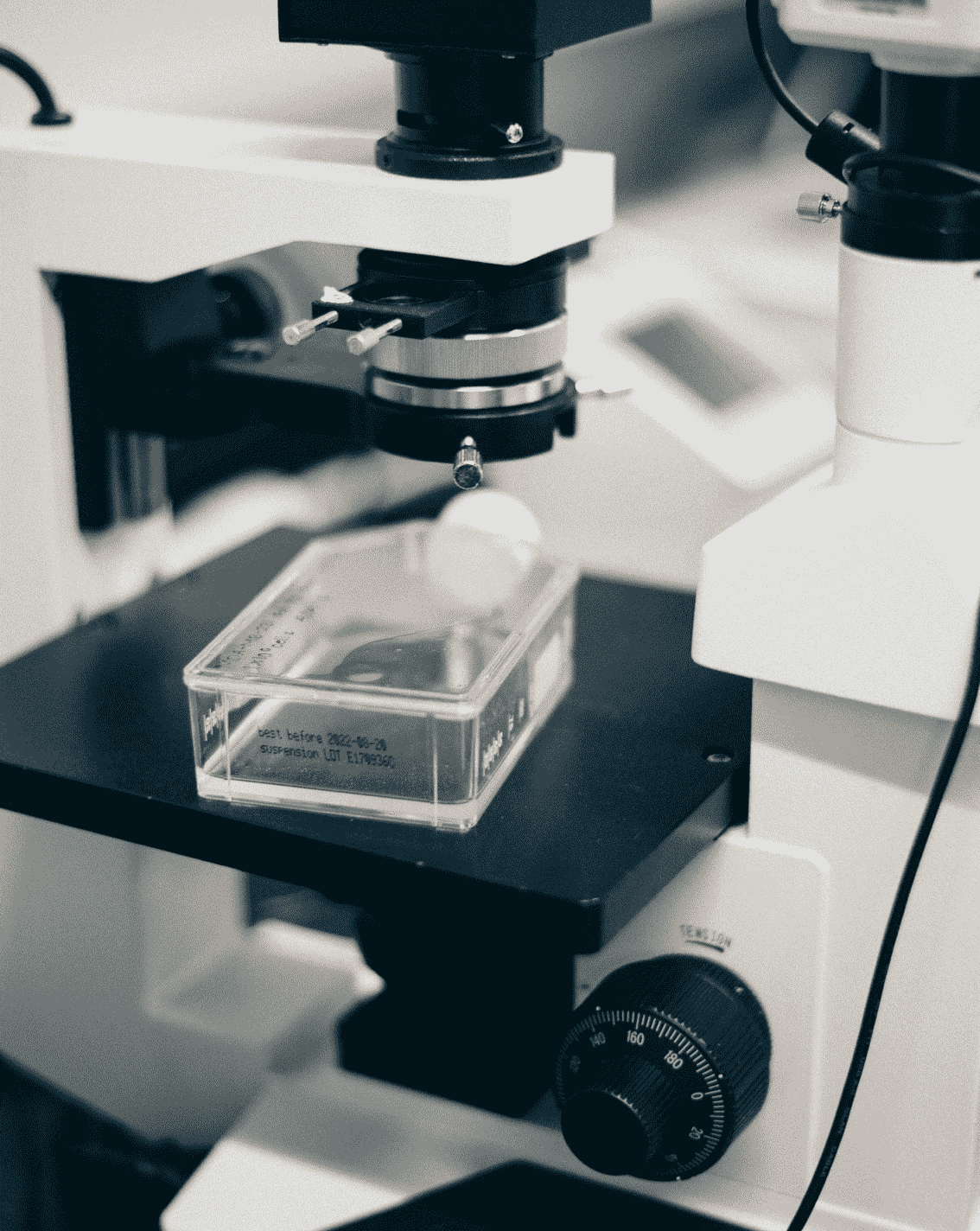
Adherent Cell Culturators utilize the property of cell attachment on the surface of the culturator, to provide the cells with an environment that mimics the growth environment in an organism. Cells attach and proliferate on the surface of the incubator to form monolayer or multilayer structures for various biomedical research.
- Types
According to the material and structure, the adherent cell cultures can be classified into the following types:
(1) Plastic Petri dishes: commonly used in the form of round, square and hexagonal shapes, suitable for large-scale cell culture.
(2) Glass culture flasks: with good light transmission and chemical stability, suitable for cell observation and long-term culture.
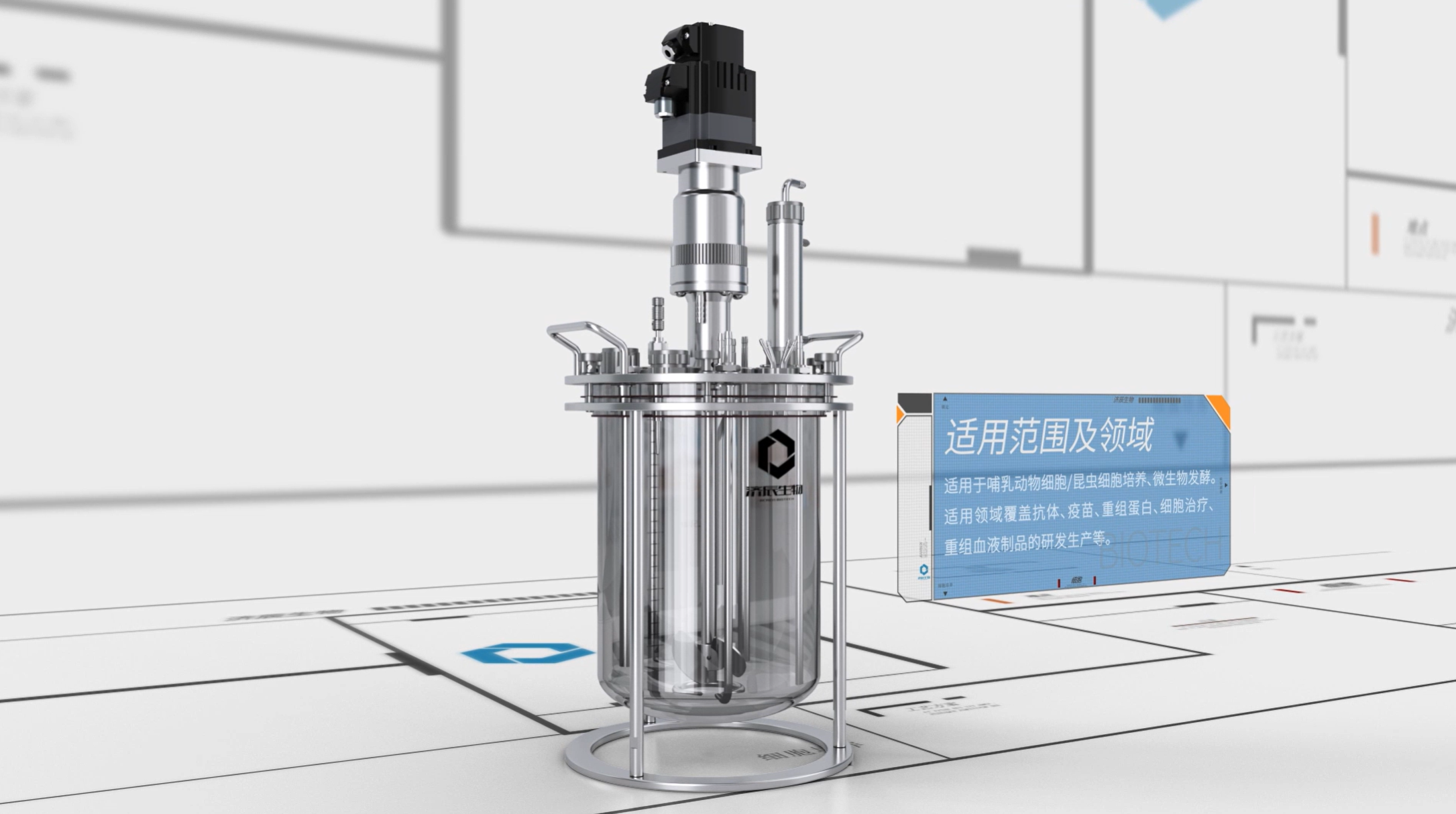
(3) Microcarrier culture system: improve the density of cell culture by microcarriers, suitable for mass production.
(4) Tissue engineering scaffolds: mimic extracellular matrix for three-dimensional cell culture and tissue construction.
Challenges of adherent cell culturators in biomedical applications
- Uneven cell attachment and spreading
Cell attachment and spreading on the surface of the culturator is influenced by a variety of factors, such as surface tension, electrical charge, and hydrophilicity. Uneven cell distribution can affect the accuracy of experimental results.
- Difficulty in cell detachment and passaging
In the process of cell passaging, how to effectively detach cells from the surface of the culturator and maintain their viability is a challenge.
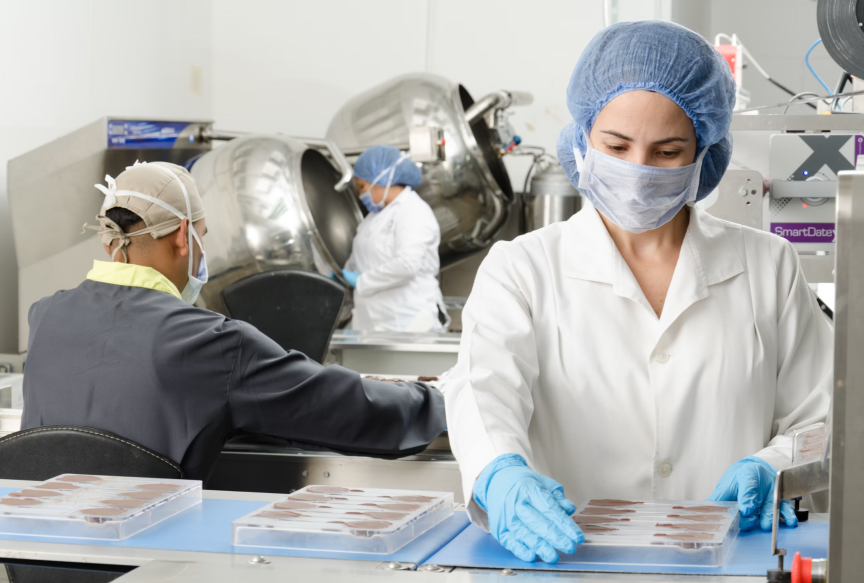
- Cell contamination and quality control
Cell cultures are susceptible to contamination by microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi, which can affect the experimental results. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure the sterility and quality of cell cultures.
- Optimization of culture conditions
For different types of cells, the culture conditions need to be optimized, such as temperature, humidity, and oxygen concentration for optimal cell growth.
Applications of Adherent Cell Culturators in Biomedicine
- Drug screening and R&D
Pasteurized cell cultures provide efficient experimental platforms for drug screening, which helps to discover novel drugs and therapeutic strategies.
- Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine
Using adherent cell cultures, researchers can construct biologically active tissues and organs in vitro to provide alternatives for clinical transplantation.
- Disease modeling
With wall-plastered cell cultures, the onset and progression of a wide range of diseases can be simulated, providing an important basis for disease research and treatment.
- Immunology Research
Applications of adherent cell cultures in immunology research include cellular immune response, antibody production, and vaccine development.
Development prospects
- New material research and development
With the development of material science, new biocompatible materials will continue to emerge, providing more choices for the adherent cell cultures.
- Microfluidics
The application of microfluidics in adherent-wall cell culturators is expected to realize the automation, precision, and high throughput of cell culture.
- Three-dimensional culture technology
Development of three-dimensional cell culture technology to simulate the growth environment of the cells in vivo, and to improve the realism of cell culture.
- Interdisciplinary Research
Research on adherent cell culturators will involve a wide range of fields such as biology, materials science, chemistry, engineering, etc., to promote interdisciplinary cooperation and innovation.
In conclusion, the adherent cell culturator has a wide range of applications in the biomedical field. Through continuous technological innovation and interdisciplinary cooperation, it is expected to make greater contributions to human health.